How to Use Tubular Lock Picks
2024-12-28 16:44
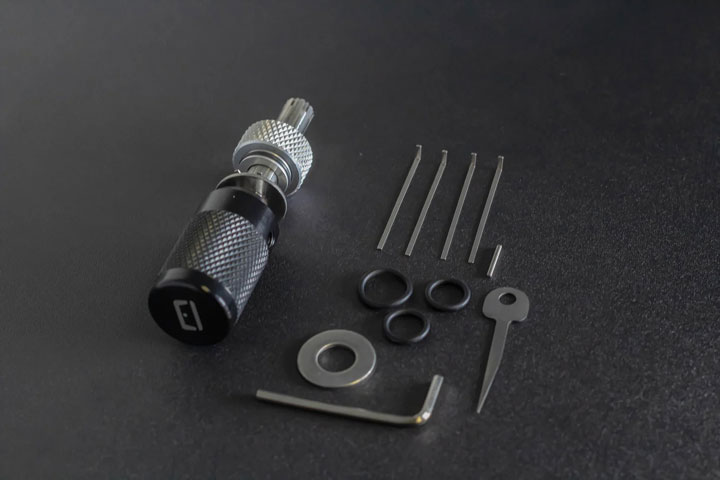

Tubular locks, known for their distinctive circular design and robust security features, are commonly found in vending machines, bike locks, and other applications where a compact yet secure locking mechanism is required. These locks differ significantly from traditional pin tumbler locks, necessitating specialized tools and techniques for opening them without the original key. This article provides an in-depth guide on how to use tubular lock picks effectively, ensuring that you can approach these locks with confidence while adhering to legal and ethical guidelines.
Understanding Tubular Locks
Before delving into the specifics of using tubular lock picks, it's crucial to understand the structure of a tubular lock. Unlike conventional locks that operate on a linear axis, tubular locks feature a series of pins arranged around the circumference of the cylinder. Each pin must be lifted to its correct height simultaneously for the lock to open. The number of pins can vary, but typically ranges from six to nine. The core of the lock rotates only when all pins align perfectly with the shear line, allowing the cylinder to turn.
Tools Required for Tubular Lock Picking
To successfully pick a tubular lock, you will need the following tools:
1.Tubular Pick: A specialized tool shaped like a small rod with a bent tip. It is designed to fit inside the cylindrical hole of the lock.
2.Tension Wrench (or Tension Tool): Used to apply rotational tension to the lock cylinder, simulating the action of turning the key.
3.Rubber Band or Spring Clamp: Sometimes used to maintain constant tension on the lock during picking.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Tubular Lock Picks
1.Prepare the Lock:
●Ensure you have permission to practice on the lock. Unauthorized lock picking is illegal and unethical.
●Familiarize yourself with the lock's structure by examining it closely. Identify the number of pins and their positions.
2.Apply Tension: Insert the tension wrench into the keyhole and apply gentle rotational pressure in the direction that would normally unlock the lock. This tension is essential as it holds the pins in place once they reach the correct height.
3.Insert the Tubular Pick: Carefully insert the tubular pick into the keyhole. The bent tip should face upward to engage the pins properly.
4.Lift the Pins:
●Begin lifting each pin individually. Start from one end and work your way around the circumference. Apply slight upward pressure to lift each pin until you feel a click or resistance indicating that the pin has reached the shear line.
●Continue this process for all pins, ensuring each one is set correctly. Patience is key here, as it may take several attempts to get all pins aligned.
5.Check Alignment:
●Once all pins appear to be set, gently increase the tension on the tension wrench. If all pins are correctly aligned, the lock should turn smoothly, unlocking the mechanism.
●If the lock does not turn, recheck the alignment of each pin and make adjustments as necessary.
6.Practice and Refinement:
●Tubular lock picking requires practice to master. Experiment with different techniques and pressures to find what works best for you.
●Consider practicing on training locks or simulated devices specifically designed for learning lock picking skills.
Advanced Techniques
For more experienced users, there are additional techniques that can enhance the effectiveness of tubular lock picking:
●Bumping: This method involves using a specially cut bump key or a modified tubular pick to rapidly strike the pins, causing them to momentarily align. When combined with applied tension, bumping can sometimes open the lock quickly.
●Raking: Similar to bumping, raking involves inserting a rake-style pick into the lock and moving it back and forth while applying tension. The motion agitates the pins, potentially setting them at the shear line.
●Decoding: Some advanced tubular lock picks come with decoding capabilities, allowing you to determine the exact depth of each pin. This information can be used to create a working key or to adjust your picking technique accordingly.
Conclusion
Using tubular lock picks is both an art and a science, requiring patience, practice, and a deep understanding of the lock's mechanics. By following the steps outlined above and adhering to ethical guidelines, you can develop the skills necessary to pick tubular locks effectively. Whether for personal enjoyment, professional development, or security testing, mastering this technique opens up a world of possibilities in the realm of physical security. Remember, the responsible and lawful application of these skills ensures that you contribute positively to the locksmithing community and beyond.
 Promotion: 5% Discount Code: 5vip
Promotion: 5% Discount Code: 5vip